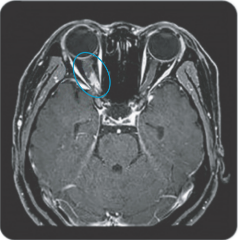
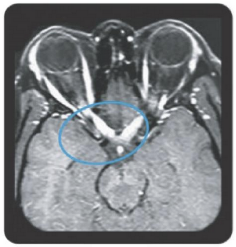
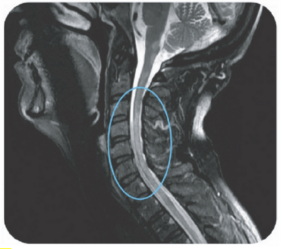
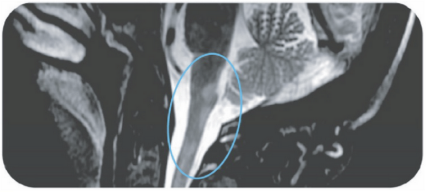
Area postrema syndrome is a core clinical characteristic of NMOSD that can appear both at disease onset and throughout the clinical course7
- The spectrum of NMOSD symptoms is broad and includes nausea, vomiting, and intractable hiccups7,8
- 4 out of 10 NMOSD attacks of the area postrema include all 3 symptoms7
- Due to symptom severity, ~80% of patients with NMOSD-related area postrema syndrome are hospitalized7